Mexico is currently facing a series of formidable water challenges, exacerbated by a historic heatwave and extended drought. These issues are caused by a combination of factors, including climate change-induced weather pattern shifts, unsustainable agricultural practices, and urban expansion.

In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into Mexico’s water challenges and explore various strategies, including cloud seeding, innovation, and water conservation efforts, to address these pressing issues.
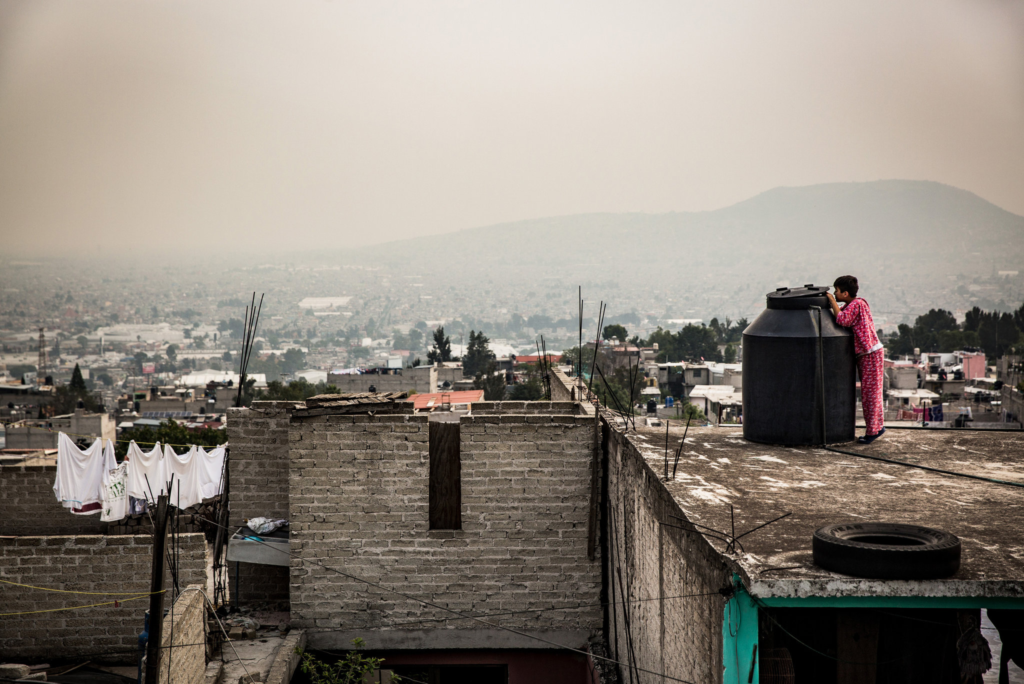
Statistics from the National Autonomous University of Mexico reveal a grim reality. Only 58 percent of Mexico’s population has daily access to running water, leaving approximately six million people without access to potable water.
Moreover, 11 million lack sanitation services, and only 14 percent of the population receives water 24 hours a day. This paints a stark picture of the dire need for action.
Mexico’s Cloud Seeding Initiative
In July, the Mexican government launched a cloud seeding initiative to increase rainfall. The process involves releasing silver iodide particles into clouds, aiming to attract additional water droplets and enhance rain or snowfall.
The initiative has successfully countered the effects of drought in rural regions, even aiding in extinguishing forest fires in 2021. However, while cloud seeding is a step in the right direction, there’s a need for more comprehensive efforts.
Innovation to Address Water Challenges
Charlie Suse from Bluefield Research emphasizes the significance of innovation in tackling Mexico’s water problems.

While innovative solutions are essential, addressing the water crisis requires substantial investments in leakage reduction, large-scale desalination, wastewater reuse, and other proven methods to reduce consumption and maximize supply.
Water Challenges in Urban and Rural Settings
a. Both urban and rural areas in Mexico face challenges in managing extreme climate events.
b. Urban areas have become heat islands due to the reduction of green spaces, while unsustainable agricultural practices have turned rural regions into desert-like wastelands.
c. The focus on ambitious projects, like cloud seeding and large-scale desalination, often overshadows fundamental water conservation strategies.
Desalination Capacities in Mexico
Between 2012 and 2022, Mexico increased its desalination capacity by an impressive 240 percent, with approximately 350 desalination plants now processing around 198 million gallons per day.

Despite this progress, cost recovery remains a concern, hindering investments in larger desalination plants.
Wastewater Reuse: A Sustainable Solution
Wastewater reuse presents another opportunity for Mexico to address its water challenges, particularly in the agricultural and industrial sectors.
Uncontrolled growth and geological disadvantages have made Mexico City one of the most densely populated and seemingly apocalyptic conurbations in the world. The city faces numerous environmental challenges, in particular its ongoing water dilemma.
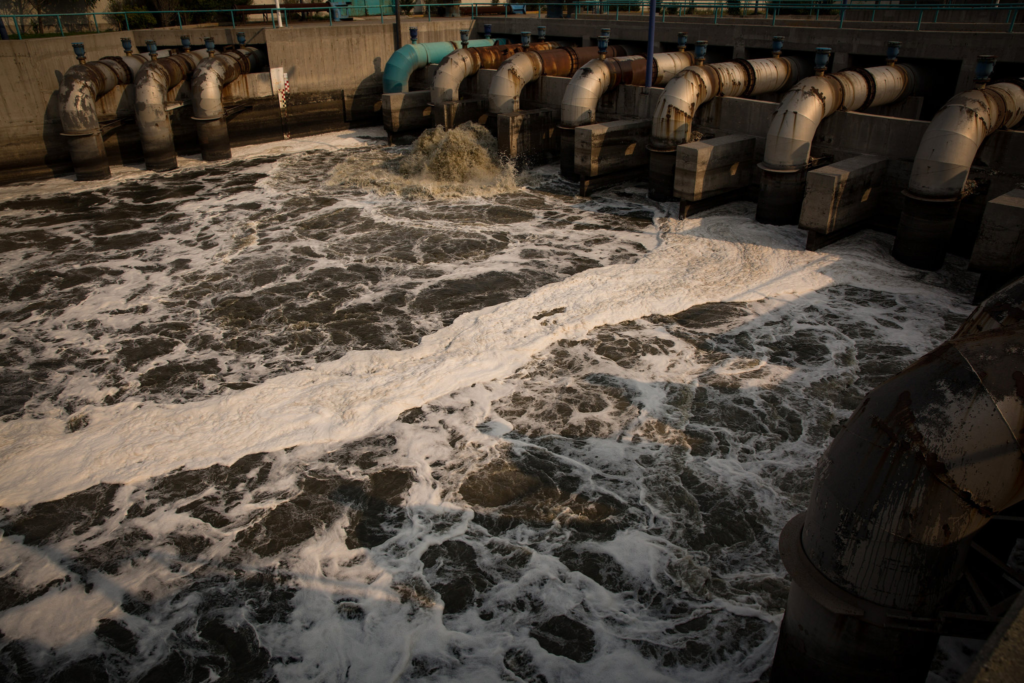

Problems include regular flooding, as aging infrastructure can no longer cope with wastewater volumes, subsidence caused by aquifer overexploitation, and the disparity between those with access to water and those without.
Major food and beverage companies, such as Unilever, are investing in water reclamation plants to meet sustainability goals and optimize water and energy usage. These initiatives can have a significant impact on water conservation and efficiency.
A Coordinated Effort for a Water-Resilient Future
Mexico’s cloud seeding initiative has shown promise in boosting rainfall and aiding aquifer replenishment. However, a more comprehensive approach is needed to address water scarcity in both urban and rural areas. This includes technology adoption, infrastructure development, conservation measures, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
The National Water Programme 2020-2024 (PNH) aims to guarantee the human right to water and sanitation, reduce vulnerability to floods and droughts, and improve water governance. With a coordinated effort, Mexico can secure a more water-resilient future for its population.
Choosing the right granular filter media

Water pretreatment in the desalination process is crucial to remove larger particles, suspended solids, and other impurities before subjecting the water to the main desalination method. While sand filters have been traditionally used in pretreatment, zeolite filter media can offer several advantages in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. The Evol
ution and Future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia
Here’s how zeolite filter media can enhance the water pretreatment process compared to sand:
- Filtration Efficiency: Zeolite has a higher filtration efficiency compared to sand due to its smaller particle size and uniformity. This allows for better removal of suspended solids and smaller particles, resulting in cleaner water.
- Ion Exchange Capacity: Zeolite’s ion exchange properties make it highly effective in removing heavy metals, ammonia, and other contaminants present in the water. It can selectively capture these ions and exchange them with less harmful ones, thereby improving water quality.
- Longer Filter Run Times: Zeolite filter media tends to have longer filter run times compared to sand filters. This means that the zeolite filters require less frequent backwashing or regeneration, reducing water and energy consumption during the pretreatment process.
- Reduced Pressure Drop: Zeolite’s smaller particle size and uniformity contribute to a lower pressure drop across the filter media. This helps maintain a consistent flow rate, reducing the energy requirements of the pretreatment system.
- Compact Design: Zeolite filters can achieve the same or higher levels of pretreatment efficiency as sand filters while requiring a smaller footprint. This compact design is especially beneficial in situations where space is limited.
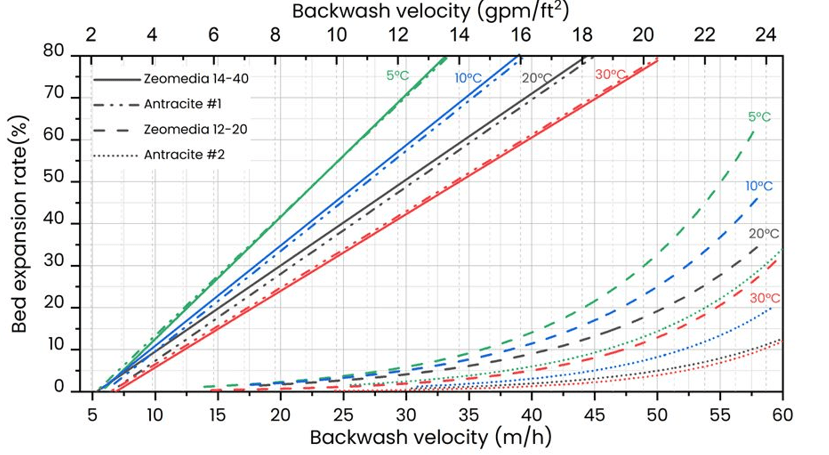
It’s worth noting that the specific design and configuration of the pretreatment system, including the type and size of zeolite media, will depend on the water source, quality, and the desalination process employed. The Role of Zeolite Filter Media The Evolution and Future of Water Desalination in Saudi Arabia