Authors: Leonardo Courtade Alvarez (Director general, ZEOMEX), Jair Rangel-Sequeda (Investigación y desarrollo de productos, ZEOMEX), Ph.D Celestino-Odín Rodríguez-Nava (Profesor titular, Instituto Politécnico Nacional) Zeolite for low carbon footprint pretreatments
Reverse osmosis
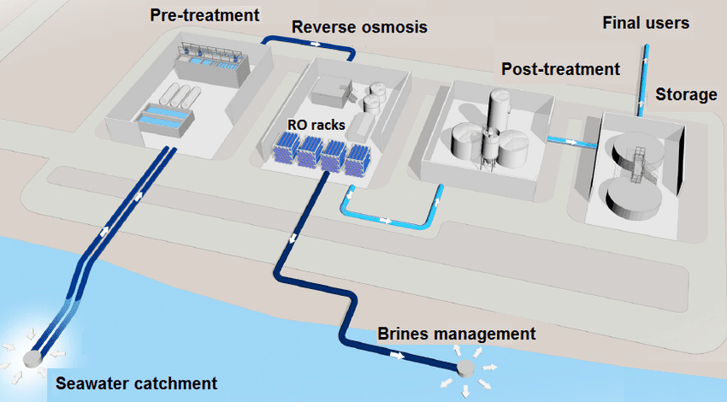
Figure 1 Diagram of the typical industrial seawater reverse osmosis (RO) desalination plant
1(Pérez-Zuñiga et al., 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8091100)
| Operational Block | Operational Cost (%) |
| Pretreatment | 15-20 |
| Reverse Osmosis System | 50-60 |
| Storage and Distribution | 5-10 |
| Wastewater Treatment | 5-10 |
| Monitoring and Control | 5-10 |
| Spare Parts and Maintenance | 10-15 |
Table 1 Distribution of average operating costs in reverse osmosis desalination plants
Zeolite for low carbon footprint pretreatments I Pre-treatment system
| Process | Capacity (m3/d) | Pretreatment system |
| UF | 10,178,509 | As standalone UF or combined with Coagulation-Flocculation, DAF, DMF, MF, Anti Scaling Inhibition, Single-stage Sand Filtration, Acidification, Sedimentation, or Disinfection. |
| DAF | 5,265,871 | As standalone DAF or combined with Coagulation-Flocculation, DMF, UF, MF, Multi-media Filtration (MMF), or Single Stage Sand Filtration. |
| DMF | 5,265,368 | As standalone DMF or combined with Coagulation-Flocculation, Sedimentation, DAF, UF, MF, or Two Stage Sand Filtration, Acidification, or Anti Scaling Inhibition. |
| MF | 2,634,964 | As standalone MF or combined with Coagulation-Flocculation, DAF, DMF, Anti Scaling Inhibition, Single-stage Sand Filtration, Acidification, Sedimentation, or Disinfection. |
| Sand filtration | 1,046,195 | As standalone Single-stage or Two-stage Sand filtration or combined with Coagulation-Flocculation, Anti Scaling Inhibition, Sedimentation, Acidification, DMF, UF, MF, MMF, or Disinfection. |
Table 2 Pretreatment methods employed in current RO desalination plants and cumulative capacities served by these methods
2 (Eke J. et al.,2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal)2020.114633
Pre-treatment system (Filtration)
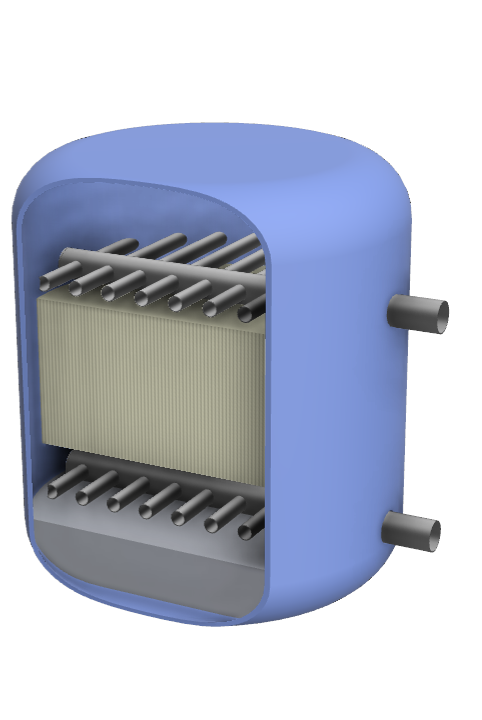

•Compact design for installation in small spaces
•High capacity for retaining suspended solids and sediments
•Ability to remove particles as small as 5 microns
•High water flow rate
•Easy operation and maintenance
•Can be equipped with different types of filtering media according to the specific needs, such as sand, activated carbon, zeolites, among others
•Robust and corrosion-resistant construction
•Provides high-purity water as feed for the next treatment stage
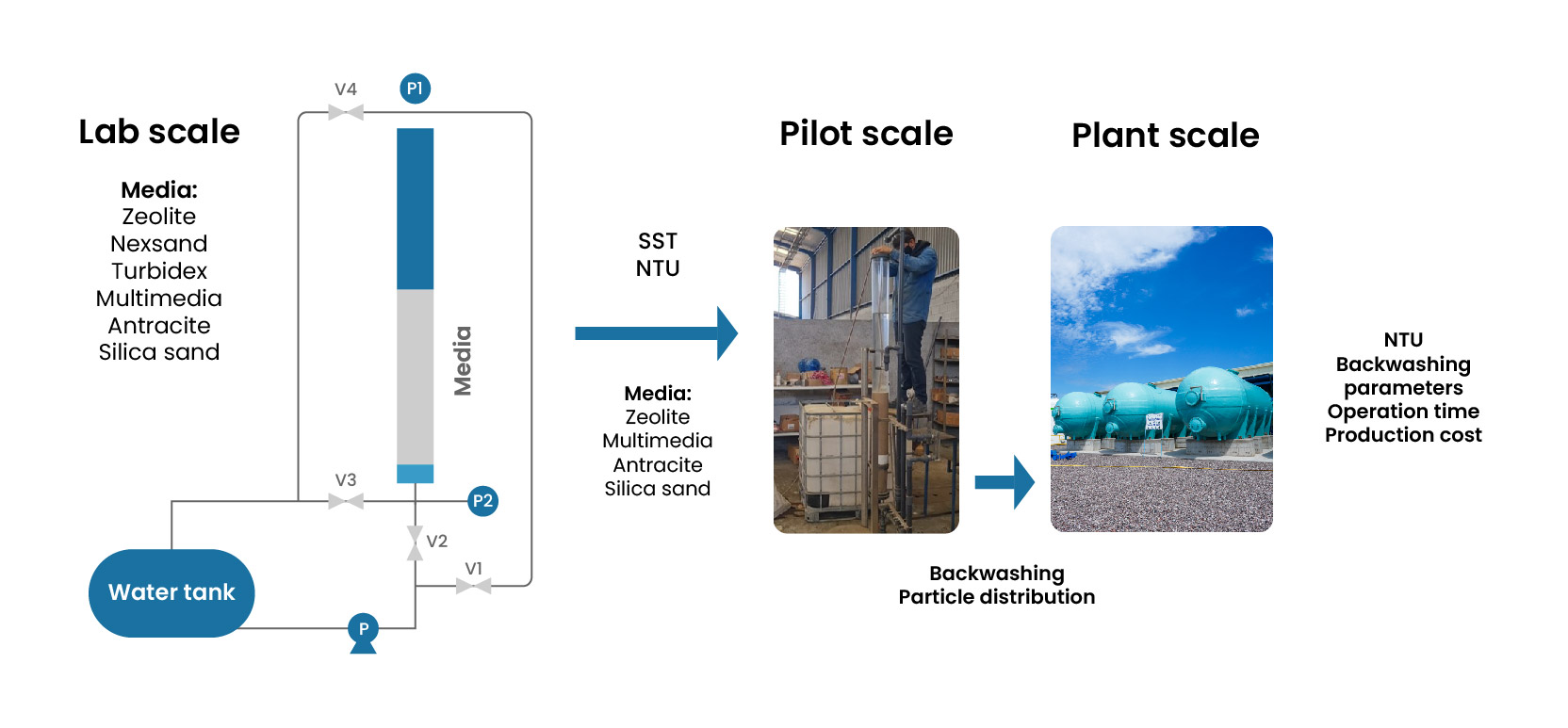
Methodology
Results (Lab scale)
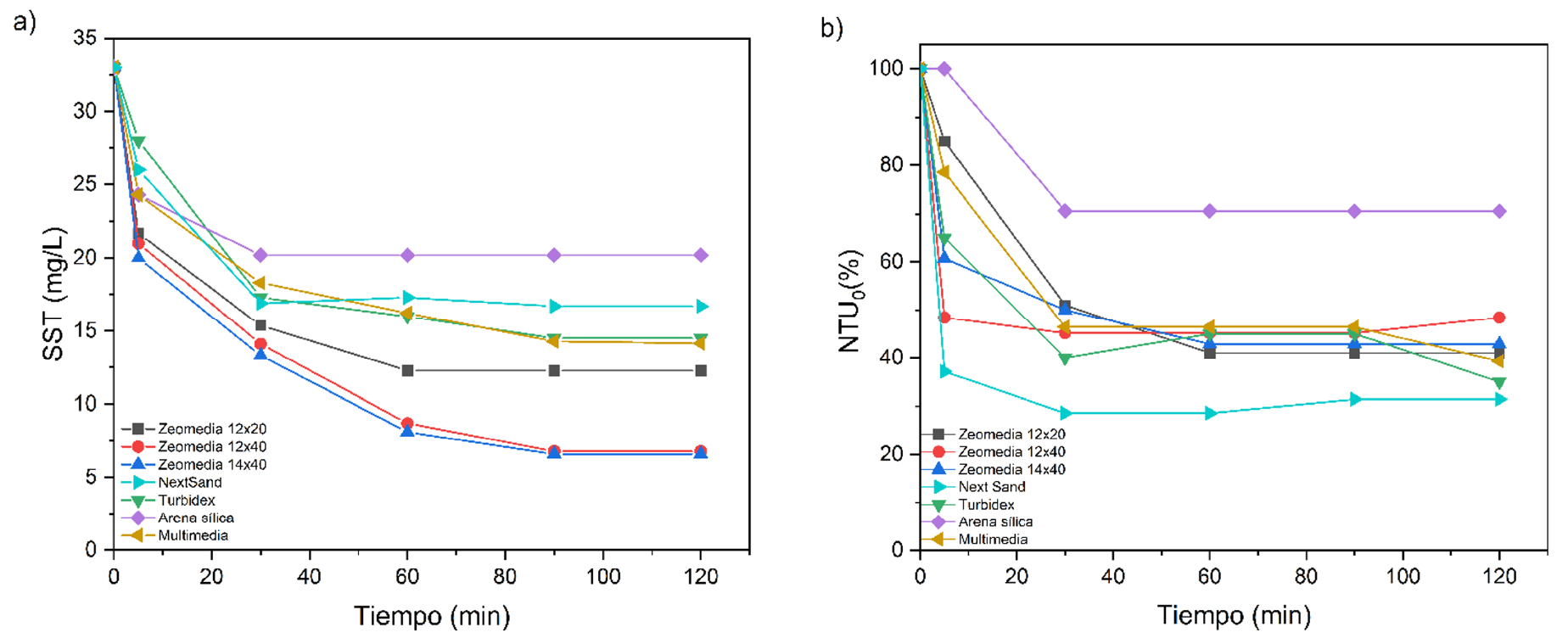
Figure 2 Reduction efficiency a) SST and b) NTU of different filter media.
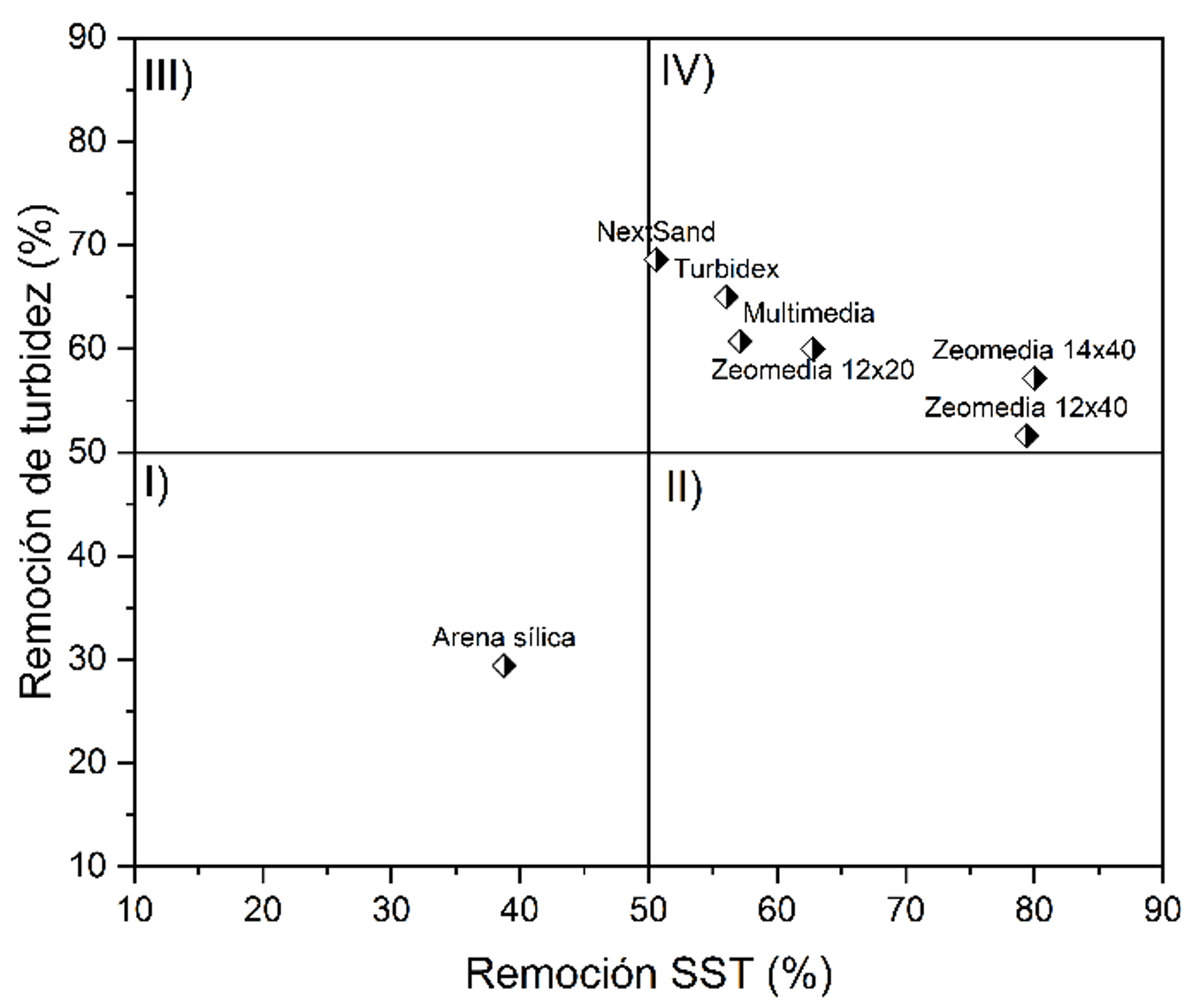
Figure 3 Correlation SST vs NTU of different filter media
| Media | Particle diameter mean (µm) | Bulk density (Kg/m³) |
Uniformy coeficient | Surface area (m²/g) |
| Zeomedia 14-40 |
915 | 720 | 1.27 | 34.8 |
| Zeomedia 12-40 |
1050 | 720 | 1.77 | 34.8 |
| Zeomedia 12-20 |
1260 | 720 | 1.55 | 34.8 |
| NextSand | 805 | 980 | 1.99 | 26.5 |
| Turbidex | 1015 | 906 | 1.29 | 25 |
| Silica sand | 311 | 1520 | 1.5 | 3.1 |
| Multimedia (70% silica sand,15% antracite, 15% support gravel) |
1050 | – | – | – |
Table 3 Textural properties of filter media used
Results (Pilot scale)
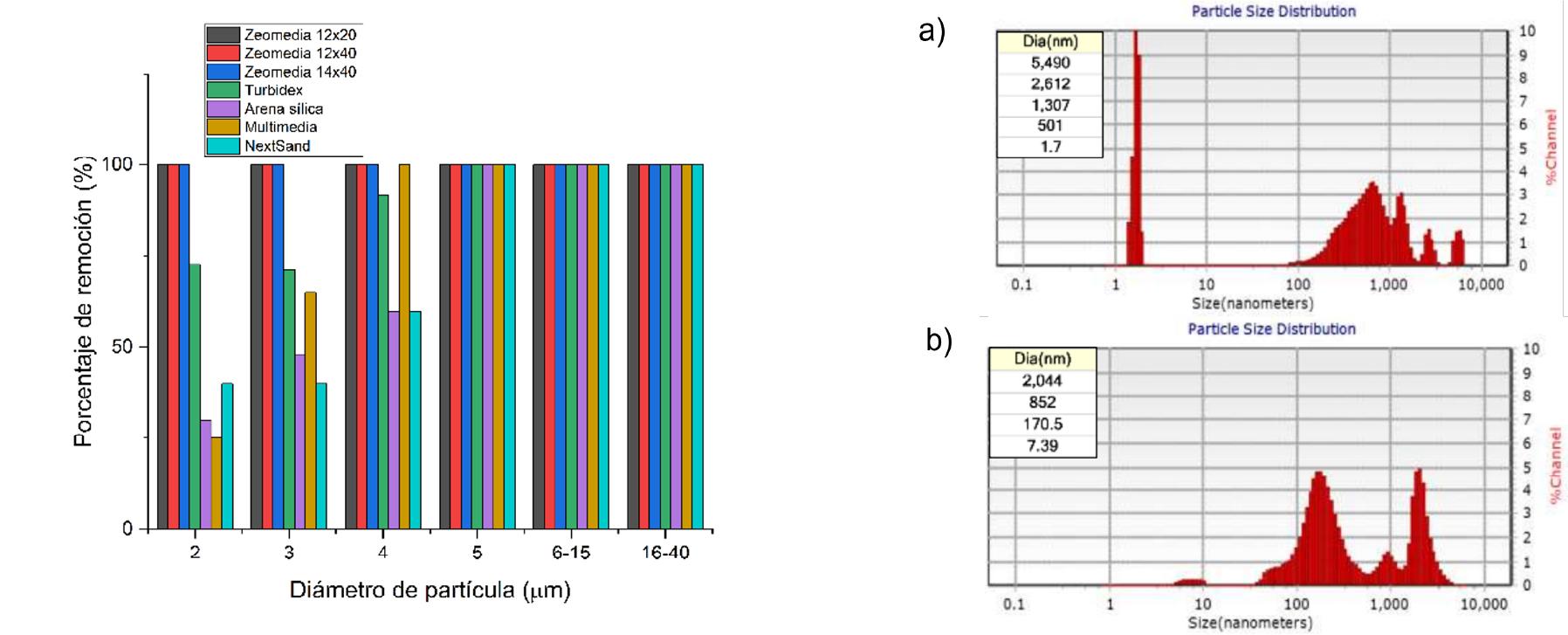
Figure 4 Distribution of particles in suspension of a) influent, b) effluent and c) percentage removal of different sizes in filter media.
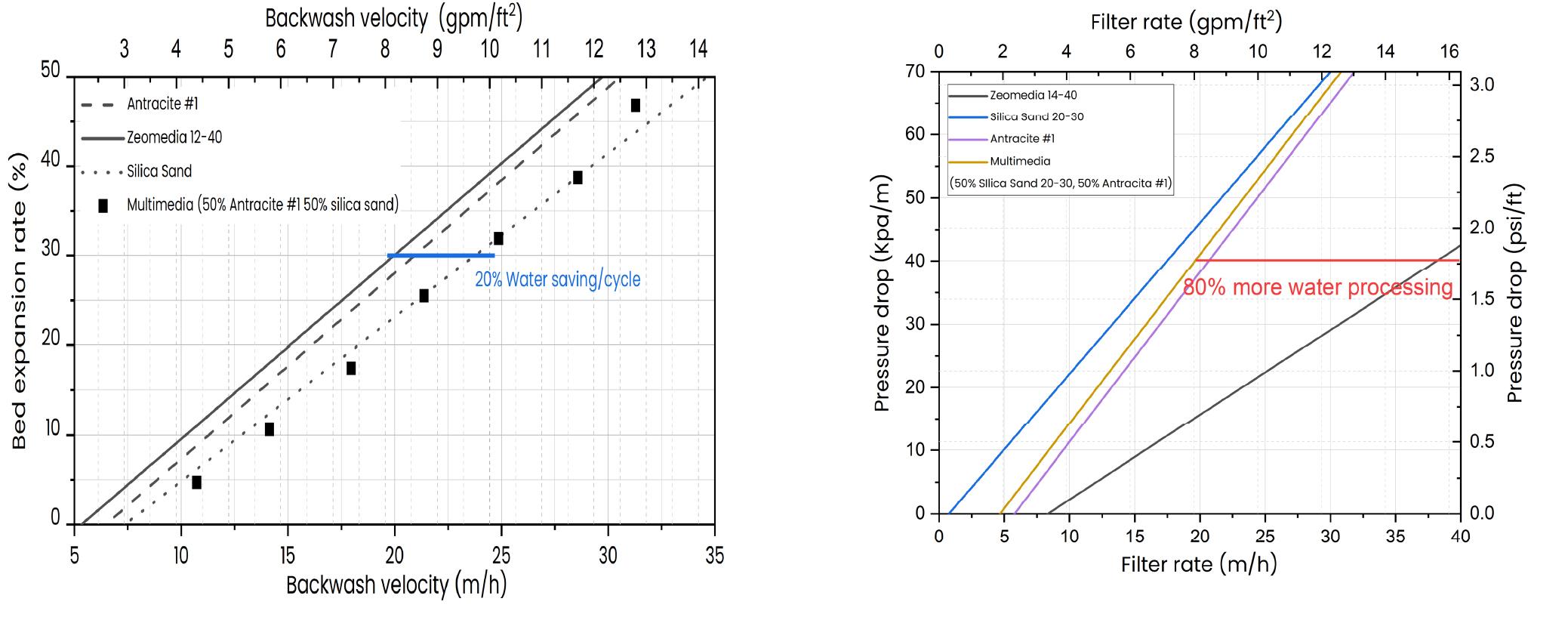
Figure 5 a)Backwashing and b) Pressure drop of different filter media and at pilot scale 25°C
Results (Plant scale)
Altavista Plant

|
Media |
Silica Sand |
Zeomedia 14×40 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
4.5 |
3.1(-31.2%) |
|
Filtration time (h) |
23.5 |
48 (+104%) |
|
Backwash time (min) |
10 |
8 (-20%) |
|
Backwash Flow rate (m3/min) |
28.3 |
28.3 |
|
Backwash water volume(m3) |
283 |
226.4 (-20%) |
|
Number of backwashes (1/year) |
372.8 |
182.5 (-104%) |
|
Backwash water volume per year (m3) |
1.26×106 |
0.49×106 (-61%) |
Table 4 Comparison of filter #4 Altavista plant with different filter media
Increase 12.5 l/s filter rate (+20%)
Water saving 384,462.5 m³/year (+30.4%)
Work in progress
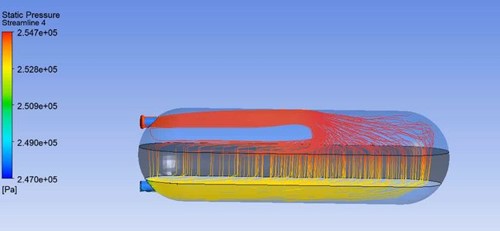
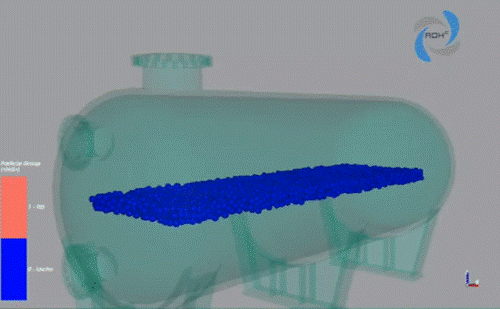
Conclusions
The results of the laboratory scale filtration tests indicate that the zeolite filter beds had a higher solids and turbidity removal capacity compared to conventional silica sand beds and were comparable to multi-bed beds.
Zeomedia zeolite presented a higher efficiency compared to other zeolitic filter materials, achieving up to 80% particle removal on a laboratory scale, as well as a cut-off rate of retention of particles smaller than 5 microns compared to conventional media.
Pilot scale fluidization tests demonstrated bed expansions similar to conventional media used in desalination plants. This gives an opportunity to change the filter material for one with higher performance without major modifications in the filter backwash systems.
The real performance of the zeolitic filters at plant scale gave an increase in filtration time and less backwash time, giving potential savings in water resources and energy compared to traditional filter media.
Thank you




Let's talk...
Tel: +52 81 3849 5959
Email: sales@zeomediafilter.com
We are the only company in Mexico with NSF certification to help you reach the new regulations and parameters marked by the new NOM 127 in the water treatment process.